Root genetics for drought and carbon adaptation: An automated system for crop plant phenotyping and soil data collection
For this ARPA-E program, Rhizosphere Observations Optimizing Terrestrial Sequestration (ROOTS), Colorado State University needed an automated process that could provide data to identify genetic variations in maize plants that affect root structure and composition. These variations can then be utilized to develop plants that exhibit a high rate of carbon sequestration into the soil. These traits also create plants with a high level of drought tolerance. The ROOTS program goals were to support development of new technologies to identify plant variants that improve soil carbon accumulation (≥50%), increase water productivity (≥25%), and reduce atmospheric buildup of the ozone precursor greenhouse gases carbon dioxide (CO2) and nitrous oxide (N20, ≥50%).
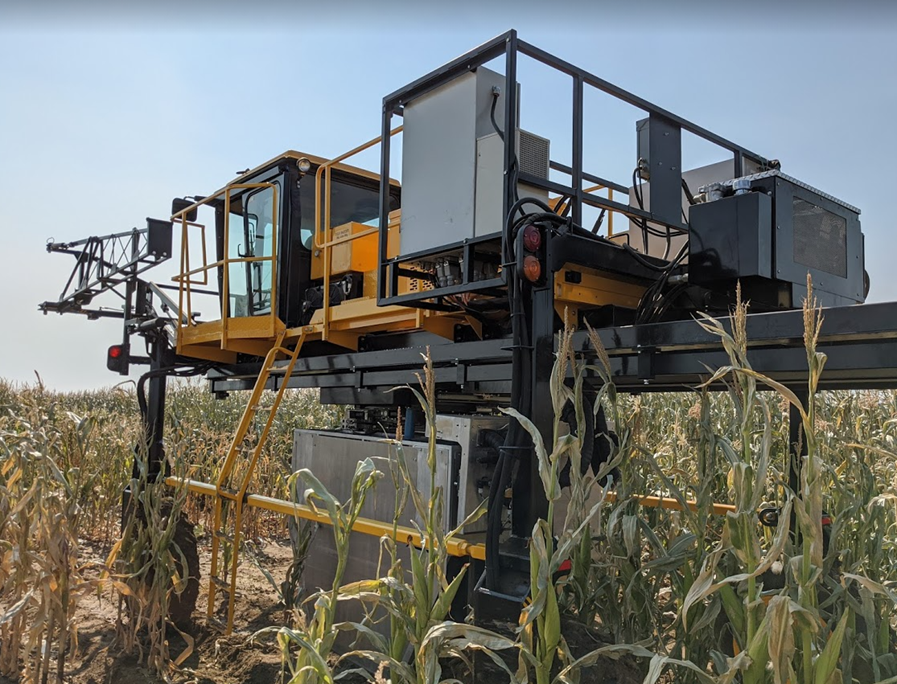


Czero's role in R&D
Czero provided a solution via the High Throughput Phenotyping (HTP) vehicle and its patent pending integrated automated root pulling system and soil sampling system. The vehicle is piloted by an operator sitting in the tractor cab that can navigate the vehicle through a planted field. Once in-field, the operator can trigger a sampling event via the onboard user interface. The fully automated event uses a vision-based plant identification system to determine the location of a plant to be sampled, then automatically moves into position, and collects data on root-pulling force. While the root pull force is being collected, a secondary system would insert a soil coring tube into the field to extract a 1meter deep soil sample. The extracted soil core would then have individual sub-samples collected and packaged at set depths of the original 1meter deep sample. These sub-samples would then be RFID tagged and stored to allow for further in-lab analysis of the soil to understand nutrient makeup and any potential carbon sequestration within the soil depths.
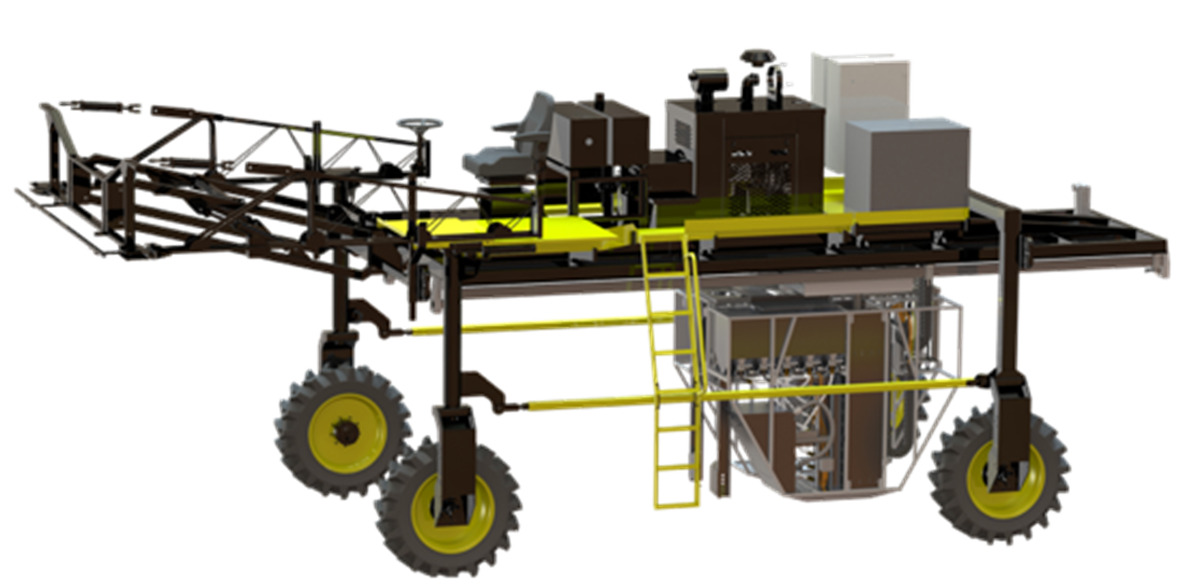
Proven Project Success
- Multiple seasons in operation with continuing Czero support.
- Use of collected data to identify specific genes contributing to root biomass and drought resistance.
- Developed an automatic plant phenotyping machine.
- Automated sampling system capable of 60+ samples per hour.
- Designed and implemented motion control on Bosch Programmable Logic Controllers to control sampling system.
- Implemented vision system to automatically locate plant stalks for sampling.
You can learn more about this and other ARPA-E ROOTS projects here.
Reach out to us, schedule a meeting, and let's find your custom solution.
We offer concept-to-prototype mechanical engineering R&D for developing systems and subsystems for cleantech innovations. Learn how we can help your team.
